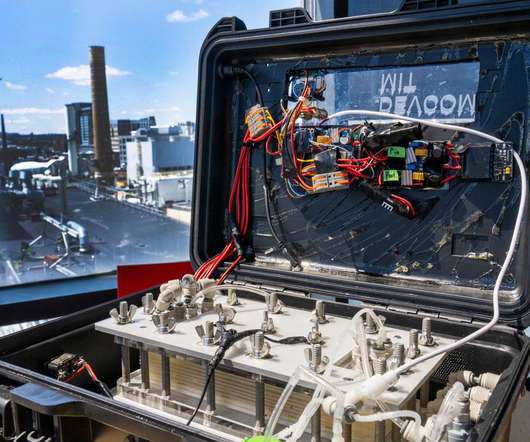
MIT scientists used solar power to make drinking water cheaper than tap water
Electrek
OCTOBER 2, 2023
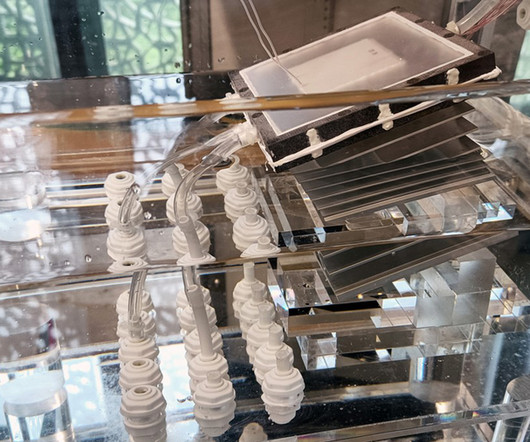
MIT scientists have designed a solar-powered desalination system that turns saltwater into drinkable water at a higher volume – and lower cost. more… The post MIT scientists used solar power to make drinking water cheaper than tap water appeared first on Electrek.







































Let's personalize your content