New Emissions Analytics study suggests pollution from tire wear now 1,850 times worse than exhaust emissions
Green Car Congress
MAY 13, 2022
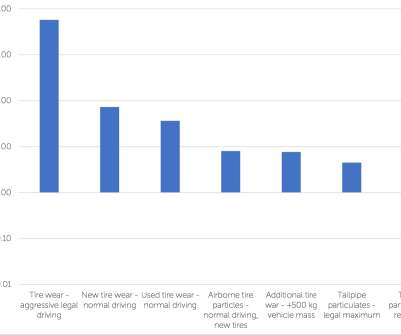
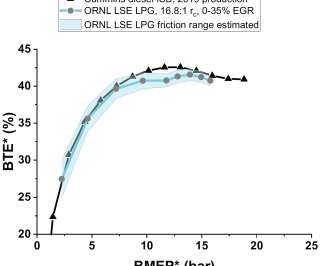
In early 2020, UK-based independent testing firm Emissions Analytics published a study claiming that tire particulate wear emissions were 1,000 times worse than exhaust emissions ( earlier post ). As testament to the filtration efficiency of the latest gasoline particulate filters (GPFs), tailpipe mass emissions are now as low as 0.02

































Let's personalize your content