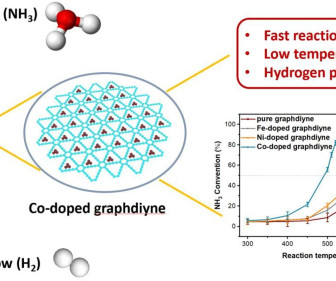
Cobalt-doped graphdiyne catalyst for catalytically decomposing ammonia to hydrogen
Green Car Congress
AUGUST 6, 2023
A team from Nanjing University, Hubei Normal University and Zhejiang University has developed a cobalt-doped graphdiyne catalyst for catalytically decomposing ammonia (NH 3 ) to generate H 2. Conversely, low-cost metal catalysts are available but demonstrate suboptimal catalytic effects.



































Let's personalize your content