MIT researchers propose mechanism for overcoming bottleneck in electroreduction of CO2
Green Car Congress
JANUARY 14, 2022
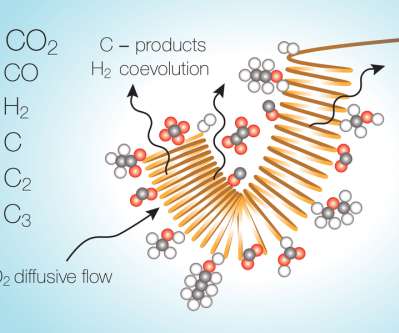
Researchers at MIT have identified , quantified, and modeled a major reason for the poor performance of electroreduction processes to convert CO 2 to fuel or other useful chemicals. The findings could spur progress on developing a variety of materials and designs for electrochemical carbon dioxide conversion systems. —Soto et al.
























Let's personalize your content