Ampcera announces a low-cost and scalable solid electrolyte technology for solid-state batteries
Green Car Congress
JUNE 24, 2020
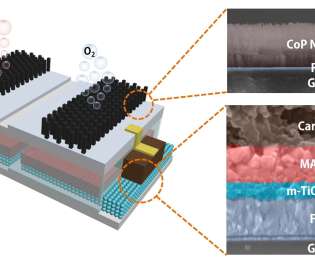
Silicon-Valley-based Ampcera announced a low-cost flexible solid electrolyte (SE) membrane technology for solid-state batteries (SSBs). Performance and cost are the bottlenecks in the commercialization of SE technology and SSBs. Hui Du, co-founder and CTO of Ampcera. Argyrodite, LGPS, LPS, LSPS, etc.);


































Let's personalize your content