Ford, U Mich study finds greater greenhouse gas reductions for pickup truck electrification than for other light-duty vehicles
Green Car Congress
MARCH 5, 2022
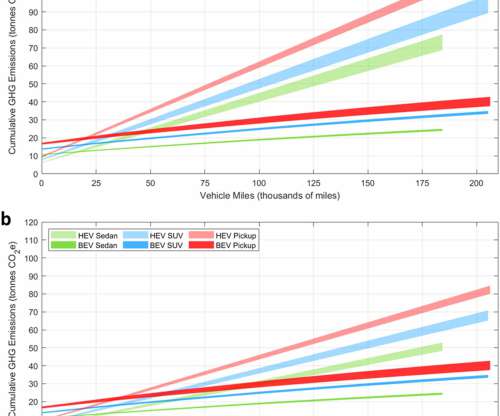
Researchers at the University of Michigan and Ford Motor Company have conducted a cradle-to-grave life cycle GHG assessment of model year 2020 ICEV, HEV, and BEV sedans, sports utility vehicles (SUVs), and pickup trucks in the United States. This is an important study to inform and encourage climate action. —Woody et al.




































Let's personalize your content