UNIST team develops novel hydrogen production process using biomass oxidation instead of water oxidation as electron source
Green Car Congress
MARCH 3, 2020
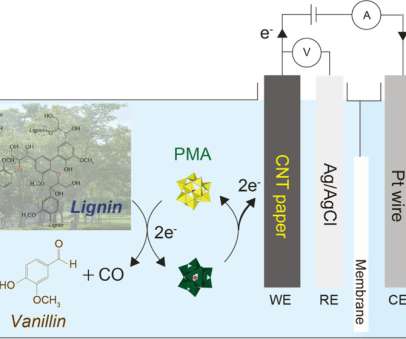
Korea’s Ulsan National Institute of Science and Technology (UNIST) have developed a novel process for the production of hydrogen using various types of biomass, including lignin, as an efficient alternative to water oxidation as an electron source. Conventionally, water is considered a cheap and clean source of electrons; 2H 2 O ?




























Let's personalize your content