Sodium-ion batteries are set to spark a renewable energy revolution – and Australia must be ready – ET Auto
Baua Electric
JULY 22, 2024
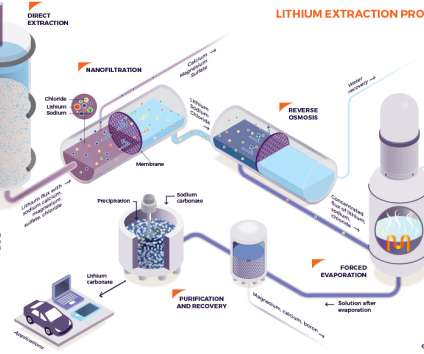
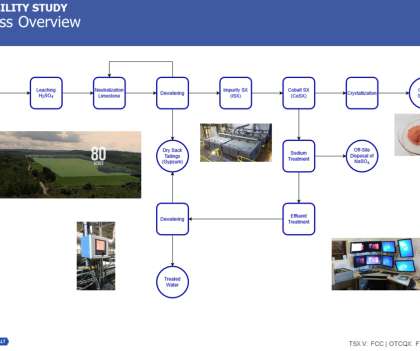
Some types of lithium mining require a lot of water and energy and have led to local pollution, such as in South America’s alpine lakes. But a new way to firm up the world’s electricity grids is fast developing: sodium-ion batteries. Sodium-ion batteries are now almost ready to fill the long-term storage gap.



















Let's personalize your content