MIT engineers create 2D polymer that self-assembles into sheets
Green Car Congress
FEBRUARY 3, 2022
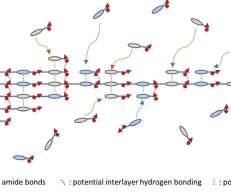
Using a novel polymerization process, MIT chemical engineers have created a new two-dimensional polymer that self-assembles into sheets, unlike all other polymers which form one-dimensional chains. Until now, scientists had believed it was impossible to induce polymers to form 2D sheets.


































Let's personalize your content