Linde and Shell team up to commercialize lower-carbon technology for ethylene: E-ODH
Green Car Congress
OCTOBER 25, 2020
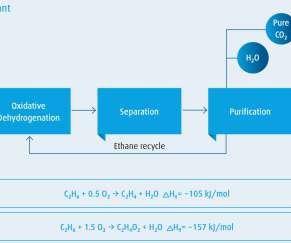
The catalytic process is an alternative route to ethane steam cracking, offering the potential of economic advantages, acetic acid co-production and significantly lower overall carbon footprint through electrification of power input. —John van der Velden, Senior Vice President Global Sales & Technology at Linde Engineering.
































Let's personalize your content