Japan team evaluates battery-assisted low-cost hydrogen production from solar energy
Green Car Congress
FEBRUARY 1, 2019
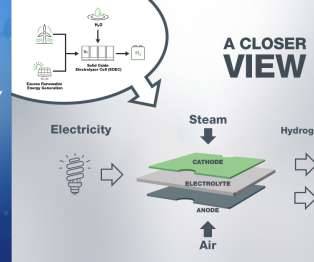
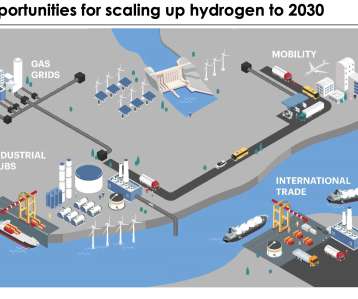
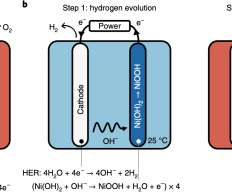
Researchers from Japan’s NIMS (National Institute for Materials Science), the University of Tokyo and Hiroshima University have jointly conducted a techno-economic analysis for hydrogen production from photovoltaic power generation (PV) utilizing a battery-assisted electrolyzer. This approximately converts to US$1.92 to US$3.00/kg

















Let's personalize your content